Guide to Know About Ventilator Machines & Infusion Pump
In the rapidly evolving field of medical technology, understanding the function and importance of various life saving devices is crucial for both healthcare professionals and the general public. Two such essential devices are the ventilator machine and the infusion pump. These machines play pivotal roles in patient care, especially in critical care units. This guide provides a comprehensive overview of these devices, shedding light on their mechanisms, uses, and significance in the medical field.
Ventilator Machine: Lifesaving Breath of Technology
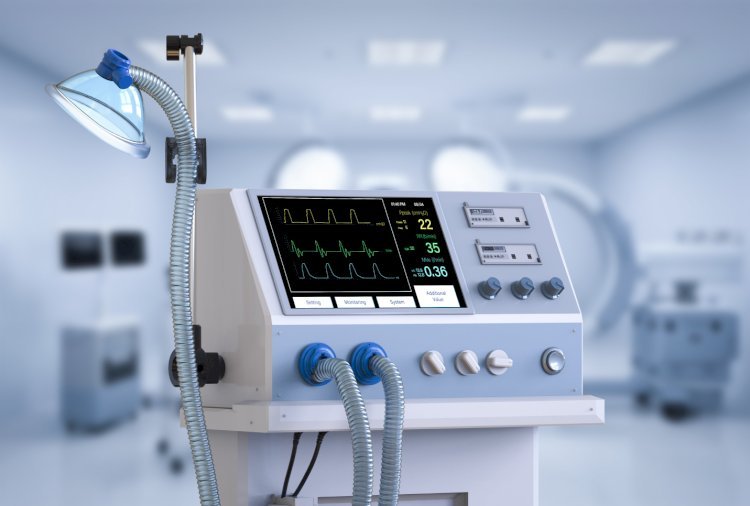
A ventilator machine is a complex yet vital medical device designed to assist or replace spontaneous breathing in patients. It is commonly used in intensive care units (ICUs), emergency rooms, and during surgical procedures. Understanding its components, functionality, and applications is crucial for appreciating its role in modern medicine.
What is a Ventilator Machine?
A ventilator machine, also known as a mechanical ventilator, is designed to move breathable air into and out of the lungs. This process assists patients who are either unable to breathe on their own or require additional respiratory support. Conditions necessitating the use of a ventilator machine include severe respiratory illnesses, surgeries, or trauma that impairs lung function.
Components and Functionality
- Control System: The brain of the ventilator, controlling the mode and timing of airflow.
- Oxygen Source: Provides a consistent supply of oxygen to the patient.
- Ventilator Circuit: Tubing that delivers air between the machine and the patient.
- Humidifier: Ensures the air provided is at the correct moisture level to protect the patient’s airways.
- Alarm System: Alerts healthcare professionals to disruptions or malfunctions.
How Does a Ventilator Machine Work?
A ventilator machine operates by cycling between two phases: inhalation and exhalation. Multiple modes can be set depending on the patient's requirements:
- Controlled Mechanical Ventilation (CMV): Delivers set breaths at predetermined intervals.
- Assist-Control Ventilation (ACV): Helps initiate a breath and ensures a minimum number of respirations.
- Synchronized Intermittent Mandatory Ventilation (SIMV): Allows spontaneous breath but ensures a pre-set number of mandatory breaths.
Applications and Importance
Ventilator machines are indispensable in numerous medical situations:
- Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome (ARDS): Helps manage severe respiratory failure.
- Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD): Provides respiratory support during exacerbations.
- Post-Surgery Care: Assists in breathing for sedated patients.
- COVID-19 Treatment: Played a critical role in the management of severe COVID-19 cases where lung function was compromised.
Infusion Pump: Precision in Treatment Delivery
An infusion pump is another pivotal device within the medical field, responsible for delivering fluids, medications, nutrients, or blood products directly into a patient’s circulatory system. The precision and reliability of infusion pumps significantly improve patient outcomes, particularly in critical care settings.
What is an Infusion Pump?
An infusion pump is a medical device used to deliver controlled amounts of fluids into a patient’s body. It ensures the precise administration of treatments over a specific period, which is critical in various therapeutic scenarios including chemotherapy, pain management, and hydration therapy.
Types of Infusion Pumps
- Volumetric Infusion Pumps: Deliver large volumes of fluid and are often used for hydration or nutritional support.
- Syringe Pumps: Used for delivering smaller volumes with high precision, typically in neonatal or intensive care units.
- Ambulatory Pumps: Portable pumps designed for patients requiring continuous medication on the go.
How Does an Infusion Pump Work?
Infusion pumps are programmed to deliver fluids at a specific rate and volume. The rate can be set in milliliters per hour (ml/h) to ensure accurate delivery of the prescribed therapy. Advanced models have sensors and alarms to detect air bubbles, occlusions, or deviations from the set delivery rate.
Importance and Applications
Infusion pumps are crucial in many therapeutic domains:
- Chemotherapy: Allows for precise dosing, reducing side effects and improving treatment efficacy.
- Anesthesia: Ensures steady delivery of anesthetics during surgery.
- Pain Management: Provides controlled delivery of analgesics, particularly in post-operative care.
- Nutritional Support: Delivers total parenteral nutrition (TPN) to patients who cannot consume food orally.
Integrated Use in Healthcare
The integration of ventilator machines and infusion pumps is often crucial in critical care management. For instance, a patient on a ventilator might simultaneously require continuous medication through an infusion pump. The synergy between these devices enhances patient care, ensuring that critical and precise treatments are administered seamlessly.
Advancements in Technology
Advancements in both ventilator machines and infusion pumps have seen significant enhancements in user interfaces, alarm systems, and connectivity. Modern ventilators are equipped with advanced features like auto-adjustable settings based on the patient’s condition, graphical monitoring, and better synchronization with the patient’s natural breathing efforts. Infusion pumps now come with software updates that allow for remote monitoring, reducing the workload on healthcare staff and improving patient safety.
Conclusion
Understanding the roles and functionalities of a ventilator machine and an infusion pump highlights their importance in the modern medical landscape. These devices not only enhance the quality of care but also ensure that critical treatments are administered accurately and effectively. As technology continues to evolve, so too will the capabilities of these vital machines, further improving patient outcomes and the overall efficiency of healthcare delivery systems.
What's Your Reaction?














