How Heat Exchangers Save You Money on Energy Costs
In today's energy-conscious world, where both industries and households prioritize efficiency and cost savings, heat exchangers emerge as a crucial solution. These devices are integral to various heating, cooling, and ventilation systems, effectively enhancing their performance. Heat exchangers significantly reduce energy consumption by facilitating optimal heat transfer, leading to lower utility bills and a smaller environmental footprint, promoting sustainability.
In this blog, we’ll explore how heat exchangers work, their various types, and how they can help you save money on energy costs.
What Is a Heat Exchanger?
The mediums can be liquids, gases, or even a combination of both, and heat transfer can be used for heating or cooling purposes.
In simple terms, a heat exchanger is a bridge that transfers heat from a hot fluid to a cooler one, effectively making the best use of available thermal energy. Common applications include HVAC systems, refrigeration, industrial processes, and automotive engines.

How Heat Exchangers Work
A heat exchanger is a device that transfers heat between two hot and cold fluids without direct contact, ensuring energy transfer without contamination.
Heat exchangers use three primary methods to transfer heat:
- Conduction: Heat is transferred through direct contact between solid surfaces.
- Convection: The transmission of heat occurs when fluids move.
- Radiation: Heat is transferred through electromagnetic waves.
In most industrial and commercial settings, the process of conduction and convection is the dominant method of heat transfer within heat exchangers. These methods ensure that thermal energy is redistributed efficiently, significantly reducing energy loss.
Types of Heat Exchangers
There are several different types of heat exchangers designed for specific applications. Each type works in slightly different ways, but all share the same basic principle of transferring heat from one fluid to another.
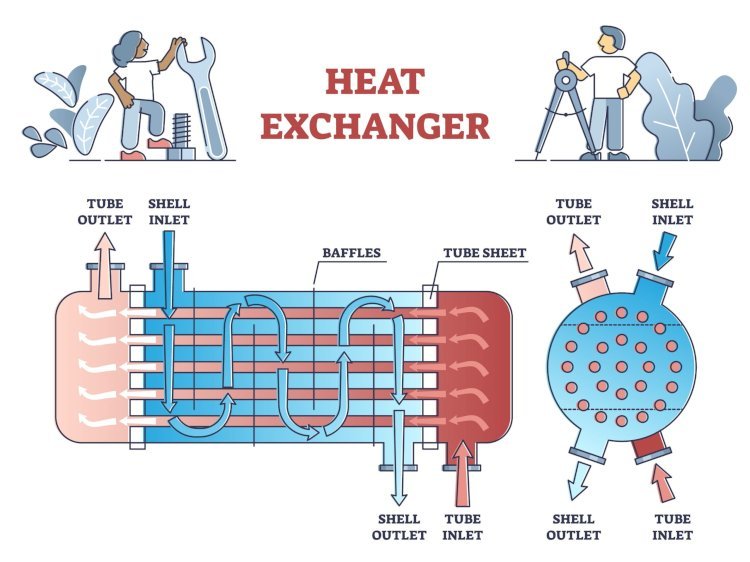
Shell and Tube Heat Exchangers
Heat exchangers are widely used in industries, consisting of tubes within a larger shell. They transfer heat from inside the tubes to outside the tubes, making them highly efficient and commonly used in power plants, oil refineries, and chemical processing plants.
Plate Heat Exchangers
Plate heat exchangers are high-efficiency systems that use thin, corrugated plates to exchange heat between fluids. They are commonly used in HVAC systems, refrigeration, and some industrial applications due to their large surface area and smaller footprint.
Air-Cooled Heat Exchangers
In air-cooled heat exchangers, the hot fluid flows through a set of tubes or plates, and air is forced over the surface of the tubes to cool the fluid. These are commonly used in systems where water is scarce or costly, such as in remote or arid locations.
Double Pipe Heat Exchangers
Double pipe heat exchangers consist of one pipe inside another, with one fluid flowing through the inner pipe and the other fluid flowing through the outer pipe. They are simpler in design than shell and tube exchangers and are often useful in smaller industrial applications or where there is space limitation.
Regenerative Heat Exchangers
In regenerative heat exchangers, both sides of exchangers use the same fluid, which allows for continuous recovery of heat. These exchangers are typically used in thermal power stations and in applications where energy recovery is a key concern.
How Heat Exchangers Reduce Energy Costs
Heat exchanger evaporator save energy by recovering and reusing waste heat, reducing the need for additional heat or cool air, thus reducing energy consumption.
Here’s how heat exchangers can save you money:
Increased Efficiency in Heating and Cooling Systems
Heat exchangers in HVAC systems enhance the efficiency of heating and cooling processes, reducing energy consumption and lowering energy bills. They transfer heat out in summer and during winter, improving comfort and reducing energy consumption in residential and commercial buildings.
Waste Heat Recovery
Heat exchangers capture excess heat from industrial processes, reducing energy consumption in industries like manufacturing, food processing, and chemical production. They use this heat to preheat other fluids, reducing the need for further heating.
Reduced Energy Loss
Heat exchangers help maximize the transmission of thermal energy between fluids while minimizing energy loss. In processes like power generation, heat exchangers help capture and reuse energy that would otherwise be wasted. Then, this energy redirects back into the system, improving overall efficiency and reducing fuel costs.
Lower Fuel Consumption
Heat exchangers in boilers and engines preheat fluids using waste heat, reducing fuel consumption and costs. This can lead to significant long-term savings for industries heavily reliant on fuel.
Sustainability and Environmental Benefits
Heat exchangers contribute to a sustainable energy system by reducing new energy production, reusing waste heat, and reducing carbon footprint. Regulations often reward energy efficiency measures, resulting in cost savings.
Applications of Heat Exchangers in Energy Cost Reduction
Heat exchangers are useful in a wide range of applications where energy cost reduction is critical. Below are some sectors where their use can provide substantial financial benefits:
- HVAC Systems: Heat exchangers optimize heat transfer in residential and commercial heating, ventilation, and air conditioning systems, reducing energy consumption and utility bills.
- Industrial Processes: Heat exchangers, utilized in chemical plants and power stations, efficiently recover waste heat, reducing fuel and electricity consumption, thereby resulting in substantial cost savings for large-scale operations.
- Renewable Energy: These are crucial in renewable energy systems like geothermal and solar power, enhancing energy efficiency by utilizing available thermal energy and reducing the need for additional power.
- Transportation: Heat exchangers in automotive systems enhance internal combustion engine efficiency and fuel consumption by capturing waste heat, and utilizing it to heat the passenger cabin or perform other functions.
How to Choose the Right Heat Exchanger for Energy Savings
Selecting the right heat exchanger and heat exchanger maker is crucial for maximizing energy savings. The selection of a heat exchanger depends on variables like:
- The fluids' respective temperatures and pressures.
- The space is available for installation.
- The maintenance requirements of the system.
- The heat exchanger's intended performance and efficiency.
Collaborating with an experienced supplier helps you select the ideal heat exchanger for your needs, ensuring long-term energy cost savings.
To Sum Up
Heat exchangers reduce energy consumption and costs by enhancing heating and cooling efficiency, recovering waste heat, and minimizing energy loss. They also offer environmental benefits like reduced fuel consumption and carbon emissions.
Investing in the right heat exchanger maker in usa and incorporating it into your energy system can provide long-lasting savings. Therefore, making it a smart choice for anyone looking to reduce their energy costs. Heat exchangers provide an efficient, sustainable solution for reducing energy costs in HVAC systems, industrial processes, and renewable energy.
AlaquaInc is a leading supplier of high-quality heat exchangers, specializing in providing energy-efficient solutions for industrial applications. AlaquaInc partners with leading U.S. manufacturers to provide thermal equipment that enhances heat transfer, cuts costs, and supports sustainability. Their expertise in heat exchange technology ensures reliable and cost-effective solutions for a wide range of industries.
What's Your Reaction?














