How Viral Infections Spread and What You Can Do to Prevent Them
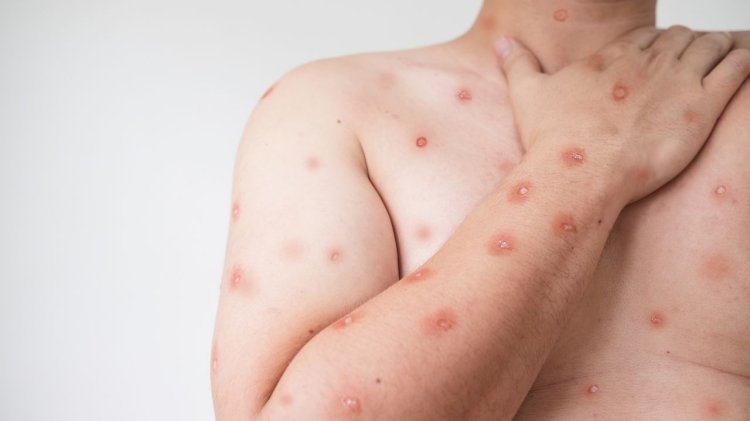
Viral infections are among the most common health threats we face today. They range from mild colds to severe diseases like COVID-19 and Monkeypox Virus Infection. Understanding how these infections spread and what you can do to prevent them is crucial for maintaining your health and the well-being of those around you.
In this blog, we will explore the mechanisms of viral transmission, common types of viral infections, and practical strategies for prevention. The goal is to equip you with the knowledge and tools to minimize risk and stay healthy.
- Understanding Viral Infections
Viral infections occur when viruses invade your body and begin to multiply. Unlike bacteria, viruses cannot survive and reproduce on their own. They must infect living cells to replicate, which often leads to disease. Viral infections can affect various body parts, including the respiratory, digestive, skin, and more.
Common Types of Viral Infections:
- Respiratory Infections include the common cold, influenza, and more severe illnesses like COVID-19.
- Gastrointestinal Infections: Viruses like norovirus and rotavirus cause these infections, leading to symptoms like vomiting and diarrhea.
- Skin Infections: Monkeypox Virus Infection and herpes are examples of viral infections that affect the skin.
- Bloodborne Infections: Hepatitis B and C, as well as HIV, are transmitted through blood and bodily fluids.
Each viral infection spreads differently, so understanding these mechanisms is critical to preventing them.
- How Viral Infections Spread
Viral infections spread through various transmission methods, each requiring specific preventive measures. Here are the primary ways viruses can spread:
1. Person-to-Person Contact
This is one of the most common ways viral infections spread. Direct contact with an infected person, such as touching, kissing, or sexual contact, can transfer viruses.
- Example: Monkeypox Virus Infection spreads through direct contact with an infected person's skin lesions or bodily fluids.
2. Airborne Transmission
Some viruses spread through the air when an infected person coughs, sneezes, or talks. These droplets can be inhaled by others, leading to infection.
- Example: Influenza and COVID-19 primarily spread through respiratory droplets in the air.
3. Contaminated Surfaces
Viruses can survive on surfaces for varying periods. Touching a contaminated surface and touching your face can introduce the virus into your body.
- Example: Norovirus causes gastrointestinal symptoms and can spread through contaminated surfaces like doorknobs and countertops.
4. Food and Water Contamination
Ingesting food or water contaminated with viruses can lead to infection. This often occurs due to poor hygiene or unsafe food handling practices.
- Example: Hepatitis A spreads through consuming contaminated food or water.
5. Animal-to-Human Transmission
Some viruses originate in animals and can be transmitted to humans through bites, scratches, or contact with animal waste.
- Example: Rabies is transmitted through the bite of an infected animal, while Monkeypox Virus Infection can spread through contact with infected animals.
- Preventive Measures for Viral Infections
Preventing viral infections requires a combination of personal hygiene, environmental control, and community-wide efforts. Here are the most effective strategies:
1. Practice Good Hygiene
Good hygiene is the foundation of preventing viral infections. Simple habits can significantly reduce your risk.
- Hand Washing: Wash your hands frequently with soap and water for at least 20 seconds, especially after being in public places, before eating, and after using the restroom.
- Use Hand Sanitizer: When soap and water are unavailable, use a hand sanitizer with at least 60% alcohol.
- Avoid Touching Your Face: Viruses can enter your body through your eyes, nose, and mouth. Avoid touching your face, particularly with unwashed hands.
2. Maintain Physical Distance
During outbreaks of respiratory viral infections, maintaining physical distance from others helps reduce the spread.
- Keep Distance: Stay at least six feet away from others in public places, especially during flu season or outbreaks of other viral infections.
- Avoid Crowded Places: Minimize your exposure to large gatherings where the risk of transmission is higher.
3. Wear Protective Gear
Wearing appropriate protective gear can prevent the spread of viral infections, particularly in high-risk environments.
- Masks: Wear a mask in crowded or enclosed spaces to reduce the risk of airborne transmission.
- Gloves: In situations where you may come into contact with contaminated surfaces, wearing gloves provides extra protection.
- Protective Clothing: Additional protective clothing may be necessary in specific cases, such as caring for someone with a viral infection like Monkeypox Virus Infection. Click here to learn more about preventive measures for Monkeypox Virus Infection.
4. Boost Your Immune System
A robust immune system helps your body fight off viral infections more effectively.
- Eat a Nutritious Diet: A balanced diet of fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains supports your immune system.
- Exercise Regularly: Physical activity promotes overall health and enhances immune function.
- Get Sufficient Sleep: Aim for 7-8 hours of quality sleep each night to support immune health.
- Stay Hydrated: Drink plenty of water to keep your body functioning optimally.
5. Vaccination
Vaccines are one of the most effective ways to prevent viral infections. They work by preparing your immune system to recognize and fight specific viruses.
- Stay Up to Date: Follow the recommended vaccination schedule health authorities provide.
- Get the Flu Shot: Annual flu vaccinations help protect against the most common strains of influenza.
- Consider Other Vaccines: Depending on your age, health condition, and travel plans, you may need vaccines for hepatitis, measles, and other viral infections.
6. Safe Food and Water Practices
To prevent foodborne viral infections, practice safe food and water handling.
- Wash Produce: Rinse fruits and vegetables thoroughly before eating.
- Cook Food Properly: Ensure meats are cooked to safe internal temperatures to kill viruses.
- Drink Safe Water: Consume water from reliable sources or use water purification methods if necessary.
7. Protect Against Animal Transmission
Take appropriate precautions if you are in an environment where animal-to-human transmission is possible.
- Avoid Contact with Wild Animals: Refrain from touching wild animals, especially in areas where viral infections are known to occur.
- Use Protective Gear: When handling animals, wear gloves and other protective gear to reduce the risk of infection.
- Keep Pets Vaccinated: Ensure your pets are vaccinated against common viral infections that could spread to humans.
- What to Do if You Suspect a Viral Infection
If you suspect you have contracted a viral infection, taking immediate action is crucial to prevent the spread and manage your symptoms.
1. Isolate Yourself
To prevent the infection from spreading, stay home and avoid contact with others as much as possible.
- Stay in a Separate Room: Use a separate bathroom if possible, and limit your contact with family members or roommates.
- Avoid Sharing Personal Items: Do not share dishes, towels, or bedding with others.
2. Seek Medical Advice
Consult a healthcare provider if you experience symptoms of a viral infection. Early diagnosis and treatment can make a significant difference.
- Call Before Visiting: If you need to visit a doctor, call ahead to inform them of your symptoms. They may provide special instructions to prevent exposing others.
- Follow Medical Guidance: Take prescribed medications as directed and follow your doctor’s advice on managing symptoms.
3. Notify Close Contacts
Inform anyone you have been in close contact with recently so they can take precautions and monitor for symptoms.
- Contact Tracing: Cooperate with any contact tracing efforts to help contain the spread of the virus.
4. Follow Quarantine Guidelines
Adhere to any quarantine or isolation guidelines provided by health authorities. Staying home for the recommended period helps prevent the spread of the infection.
- Community Efforts to Prevent Viral Infections
Preventing viral infections is not just an individual effort; it requires community-wide actions and cooperation.
1. Promote Vaccination
Encourage others in your community to get vaccinated. Herd immunity is vital in protecting those who cannot receive vaccines for medical reasons.
- Educate Others: Share accurate information about the benefits of vaccination.
- Support Vaccination Clinics: Volunteer or support local vaccination efforts.
2. Participate in Public Health Measures
Follow public health guidelines during outbreaks, such as wearing masks, practising social distancing, and adhering to travel restrictions.
- Follow Local Guidelines: Stay informed about and comply with any restrictions or guidelines issued by health authorities.
- Support Health Initiatives: Engage in or support initiatives to prevent the spread of viral infections.
3. Promote Hygiene Awareness
Raising awareness about the importance of hygiene can help prevent the spread of viral infections in your community.
- Share Information: Use social media and other platforms to share tips on hygiene and prevention.
- Teach Children: Educate children on the importance of washing hands and practising good hygiene from an early age.
Conclusion
Viral infections pose a significant threat to global health, but you can protect yourself and others by understanding how they spread and taking preventive measures. Whether practising good hygiene, getting vaccinated, or following public health guidelines, every action counts in the fight against viral infections. Stay informed, stay prepared, and contribute to a healthier, safer world.
Integrating these strategies into your daily routine reduces the risk of contracting or spreading viral infections. Remember, prevention is always better than cure. Stay vigilant and proactive in your approach to health, and encourage those around you to do the same.
What's Your Reaction?














